2% of global electricity is generated from Biofuels

Biofuels are derived from biological materials such as plant or animal matter, and they represent an innovative yet traditional way of generating low-carbon electricity. Common sources for biofuel production include crops like corn and sugarcane, crop residues, and even algae. The process of converting these biological materials into fuel generally involves either direct combustion, fermentation into ethanol, or the extraction of oils that can be converted into biodiesel. Biofuels are a versatile energy source and contribute to the decarbonization of electricity, although they are often more intensively produced in some regions than others.
To generate electricity, biofuels are employed in a variety of processes. One common method is the combustion of biomass in power plants, where the heat generated is used to produce steam. This steam then drives turbines, creating electricity. Additionally, biofuels can be converted into biogas through anaerobic digestion, which involves the breakdown of organic matter in the absence of oxygen. This biogas can then be used in gas turbines or sold as a clean substitute for fossil gas to produce electrical power. Though biofuels contribute to low-carbon electricity, their carbon intensity of 230 gCO2eq/kWh makes them less favorable when compared to other low-carbon sources like wind at 11 gCO2eq/kWh, nuclear at 12 gCO2eq/kWh, and solar at 45 gCO2eq/kWh. These sources are exceptionally low in carbon emissions and should be prioritized in our efforts to expand clean and sustainable energy.
One major disadvantage of biofuels is their relatively high carbon intensity when compared with other clean energy sources. With a carbon footprint of 230 gCO2eq/kWh, biofuels emit significantly more carbon dioxide than wind, solar, and nuclear power. Although they emit much less than fossil fuels such as coal, which releases 820 gCO2eq/kWh, and oil, which emits 650 gCO2eq/kWh, biofuels do not reach the optimal potential of minimizing carbon emissions. It is imperative for us to focus on expanding the contribution of truly low-carbon sources like wind, nuclear, and solar, which are among the most sustainable options available for electricity generation and significantly help mitigate climate change.
Another concern regarding biofuels is air pollution. The combustion of biomass can release harmful pollutants, such as particulate matter and nitrogen oxides, which can have adverse effects on air quality and human health. While cleaner than burning fossil fuels, the emissions from biofuel plants can still contribute to air pollution. Therefore, efforts should be directed toward minimizing air pollutants through advanced technologies and balancing the energy mix with the cleanest options available.
Ultimately, while biofuels play an important role in the spectrum of low-carbon energy sources, the focus should remain on significantly increasing the share of exceptionally clean electricity sources like wind, nuclear, and solar. These sources offer the most rapidly scalable and low-impact solutions to meet the growing global demand for electricity, a demand that is only set to rise as the world embraces electrification and technological advances. The growth of these clean energy sources is critical to achieving a sustainable and low-carbon future.
| Country/Region | kWh/person | % | TWh |
|---|---|---|---|
| Finland | 1770.8 W | 11.6% | 10.0 TWh |
| Maine | 1239.2 W | 11.2% | 1.8 TWh |
| Denmark | 1076.9 W | 19.6% | 6.5 TWh |
| Martinique | 715.5 W | 16.8% | 0.3 TWh |
| Vermont | 659.2 W | 6.9% | 0.4 TWh |
| Alabama | 624.0 W | 2.3% | 3.2 TWh |
| Guadeloupe | 623.9 W | 14.6% | 0.2 TWh |
| United Kingdom | 560.9 W | 12.3% | 38.7 TWh |
| Uruguay | 540.4 W | 12.8% | 1.8 TWh |
| New Hampshire | 527.6 W | 4.2% | 0.7 TWh |
| Germany | 488.9 W | 9.2% | 41.5 TWh |
| Luxembourg | 472.9 W | 6.7% | 0.3 TWh |
| Georgia (US) | 450.1 W | 3.1% | 5.1 TWh |
| Mississippi | 433.5 W | 1.6% | 1.3 TWh |
| Louisiana | 430.0 W | 1.7% | 2.0 TWh |
| Virginia | 380.9 W | 2.2% | 3.4 TWh |
| Estonia | 378.3 W | 6.7% | 0.5 TWh |
| Japan | 371.9 W | 4.7% | 45.8 TWh |
| Belize | 364.9 W | 20.5% | 0.1 TWh |
| Netherlands | 349.9 W | 5.3% | 6.4 TWh |
| Lithuania | 312.2 W | 7.1% | 0.9 TWh |
| Austria | 299.0 W | 4.4% | 2.8 TWh |
| Chile | 294.4 W | 6.6% | 5.8 TWh |
| Czechia | 290.3 W | 4.4% | 3.2 TWh |
| Singapore | 289.4 W | 2.8% | 1.7 TWh |
| Réunion | 286.9 W | 7.4% | 0.3 TWh |
| Macao SAR China | 284.0 W | 3.7% | 0.2 TWh |
| South Carolina | 280.9 W | 1.5% | 1.6 TWh |
| Canada | 274.6 W | 1.8% | 11.0 TWh |
| Portugal | 267.9 W | 4.8% | 2.8 TWh |
| Arkansas | 262.4 W | 1.3% | 0.8 TWh |
| Brazil | 254.4 W | 7.1% | 54.0 TWh |
| Mauritius | 251.3 W | 9.8% | 0.3 TWh |
| Belgium | 247.8 W | 3.7% | 2.9 TWh |
| Oregon | 245.5 W | 1.6% | 1.0 TWh |
| Idaho | 238.8 W | 1.6% | 0.5 TWh |
| South Korea | 237.5 W | 2.1% | 12.3 TWh |
| Switzerland | 234.5 W | 2.6% | 2.1 TWh |
| EU | 226.8 W | 3.9% | 102.1 TWh |
| Latvia | 213.6 W | 5.5% | 0.4 TWh |
| Minnesota | 201.6 W | 1.6% | 1.2 TWh |
| Michigan | 200.1 W | 1.6% | 2.0 TWh |
| Wisconsin | 198.1 W | 1.5% | 1.2 TWh |
| Guatemala | 190.9 W | 24.8% | 3.5 TWh |
| Thailand | 188.4 W | 5.8% | 13.5 TWh |
| Croatia | 172.2 W | 3.6% | 0.7 TWh |
| Eswatini | 170.7 W | 14.1% | 0.2 TWh |
| Ireland | 170.4 W | 2.6% | 0.9 TWh |
| Hungary | 168.5 W | 3.7% | 1.6 TWh |
| French Guiana | 167.6 W | 5.1% | 0.1 TWh |
| Slovakia | 158.5 W | 3.0% | 0.9 TWh |
| People's Republic of China | 157.8 W | 2.1% | 224.7 TWh |
| New Zealand | 154.9 W | 1.8% | 0.8 TWh |
| Rhode Island | 147.1 W | 1.7% | 0.2 TWh |
| Washington | 144.0 W | 1.1% | 1.2 TWh |
| Hawaii | 143.6 W | 1.8% | 0.2 TWh |
| Connecticut | 142.7 W | 1.2% | 0.5 TWh |
| United States | 137.8 W | 1.1% | 47.7 TWh |
| North Carolina | 133.5 W | 1.0% | 1.5 TWh |
| Nicaragua | 130.4 W | 16.2% | 0.9 TWh |
| Fiji | 129.9 W | 10.4% | 0.1 TWh |
| Florida | 129.7 W | 1.1% | 3.1 TWh |
| Malaysia | 128.9 W | 2.5% | 4.6 TWh |
| Massachusetts | 125.2 W | 1.5% | 0.9 TWh |
| Honduras | 117.4 W | 10.5% | 1.3 TWh |
| California | 115.1 W | 1.5% | 4.5 TWh |
| Pennsylvania | 112.3 W | 0.6% | 1.5 TWh |
| Spain | 110.5 W | 2.1% | 5.3 TWh |
| Australia | 107.8 W | 1.0% | 2.9 TWh |
| Italy | 102.5 W | 2.3% | 6.1 TWh |
| Turkey | 99.6 W | 2.6% | 8.8 TWh |
| El Salvador | 90.1 W | 6.9% | 0.6 TWh |
| Kentucky | 86.3 W | 0.5% | 0.4 TWh |
| France | 86.2 W | 1.1% | 5.8 TWh |
| Guyana | 84.7 W | 5.2% | 0.1 TWh |
| Indonesia | 79.9 W | 6.4% | 22.5 TWh |
| New York | 78.8 W | 1.0% | 1.5 TWh |
| Washington, D.C. | 74.4 W | 0.5% | 0.1 TWh |
| Poland | 73.8 W | 1.8% | 2.9 TWh |
| Oklahoma | 73.4 W | 0.3% | 0.3 TWh |
| The World | 72.6 W | 2.0% | 592.6 TWh |
| New Jersey | 65.2 W | 0.7% | 0.6 TWh |
| Tennessee | 63.9 W | 0.4% | 0.5 TWh |
| Belarus | 63.2 W | 1.2% | 0.6 TWh |
| Iowa | 62.2 W | 0.3% | 0.2 TWh |
| Slovenia | 59.4 W | 0.9% | 0.1 TWh |
| Alaska | 57.0 W | 0.6% | 0.0 TWh |
| Argentina | 55.7 W | 1.7% | 2.6 TWh |
| Colombia | 51.5 W | 3.1% | 2.8 TWh |
| Maryland | 51.0 W | 0.5% | 0.3 TWh |
| Norway | 48.6 W | 0.2% | 0.3 TWh |
| Serbia | 46.3 W | 0.9% | 0.3 TWh |
| Samoa | 46.2 W | 6.7% | 0.0 TWh |
| Qatar | 43.4 W | 0.2% | 0.1 TWh |
| Nebraska | 41.4 W | 0.2% | 0.1 TWh |
| Cyprus | 38.8 W | 0.9% | 0.1 TWh |
| Delaware | 36.9 W | 0.3% | 0.0 TWh |
| Paraguay | 35.1 W | 0.5% | 0.2 TWh |
| Bolivia | 33.1 W | 3.3% | 0.4 TWh |
| Montana | 33.1 W | 0.1% | 0.0 TWh |
| Malta | 31.2 W | 0.8% | 0.0 TWh |
| Cuba | 29.9 W | 2.2% | 0.3 TWh |
| Ecuador | 28.7 W | 1.6% | 0.5 TWh |
| Texas | 28.0 W | 0.2% | 0.9 TWh |
| India | 27.8 W | 2.1% | 40.7 TWh |
| Ohio | 27.2 W | 0.2% | 0.3 TWh |
| Indiana | 25.1 W | 0.2% | 0.2 TWh |
| Bulgaria | 23.6 W | 0.4% | 0.2 TWh |
| Arizona | 23.1 W | 0.1% | 0.2 TWh |
| Romania | 23.0 W | 0.8% | 0.4 TWh |
| Hong Kong SAR China | 21.5 W | 0.3% | 0.2 TWh |
| Jamaica | 21.1 W | 1.3% | 0.1 TWh |
| Illinois | 19.4 W | 0.1% | 0.2 TWh |
| Dominican Republic | 19.2 W | 0.9% | 0.2 TWh |
| Ukraine | 19.0 W | 0.7% | 0.8 TWh |
| Kansas | 18.9 W | 0.1% | 0.1 TWh |
| Peru | 18.1 W | 1.0% | 0.6 TWh |
| Utah | 18.1 W | 0.2% | 0.1 TWh |
| Nevada | 16.4 W | 0.1% | 0.1 TWh |
| Missouri | 15.9 W | 0.1% | 0.1 TWh |
| Suriname | 15.9 W | 0.5% | 0.0 TWh |
| New Mexico | 12.6 W | 0.1% | 0.0 TWh |
| Colorado | 12.5 W | 0.1% | 0.1 TWh |
| Israel | 11.9 W | 0.1% | 0.1 TWh |
| Republic of China (Taiwan) | 11.6 W | 0.1% | 0.3 TWh |
| Azerbaijan | 10.6 W | 0.4% | 0.1 TWh |
| Uganda | 9.9 W | 8.2% | 0.5 TWh |
| Costa Rica | 9.7 W | 0.4% | 0.1 TWh |
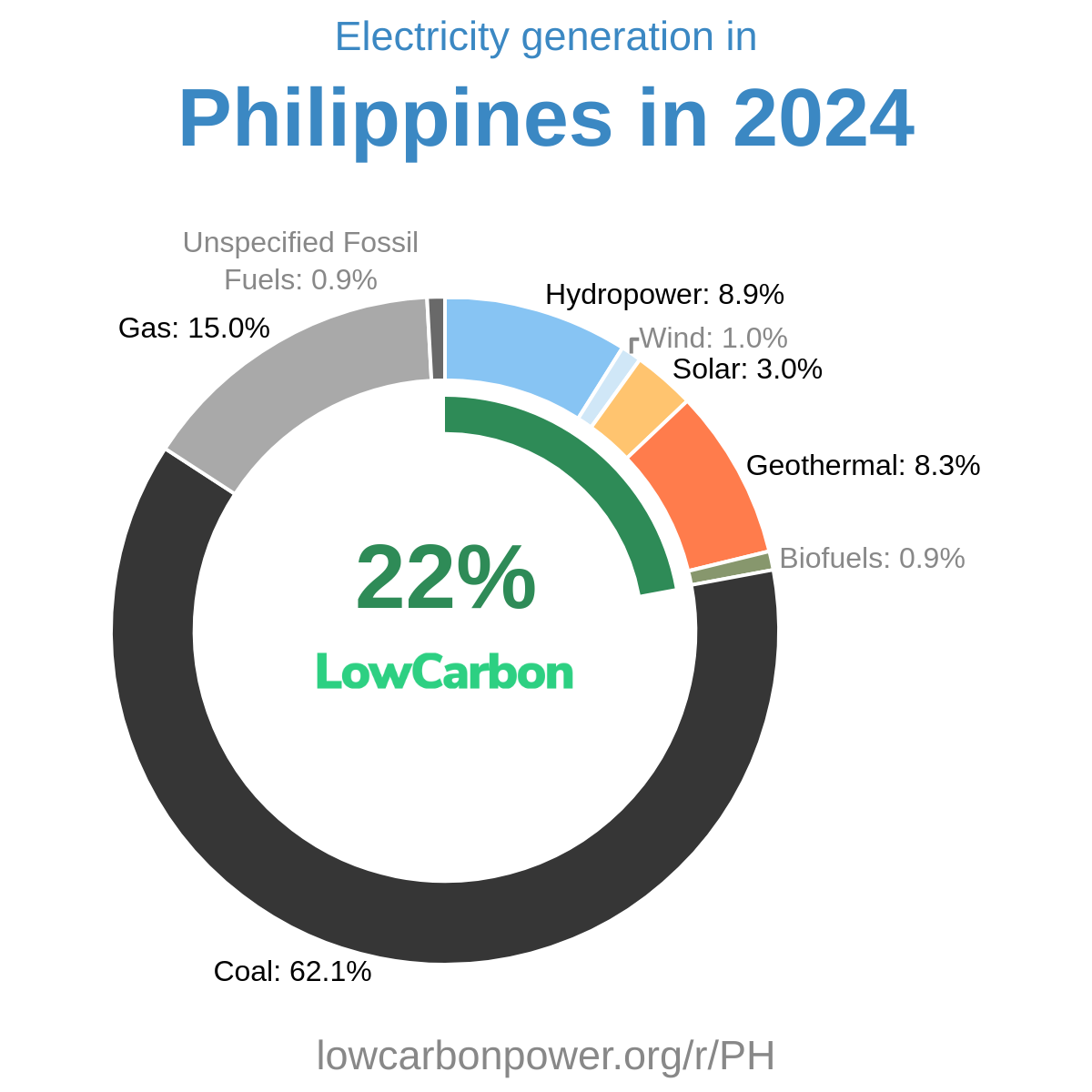
| Philippines | 9.5 W | 0.9% | 1.1 TWh |
| Panama | 9.0 W | 0.3% | 0.0 TWh |
| Vietnam | 8.4 W | 0.3% | 0.8 TWh |
| Pakistan | 7.7 W | 1.1% | 1.9 TWh |
| South Dakota | 7.4 W | 0.0% | 0.0 TWh |
| Zimbabwe | 7.3 W | 1.2% | 0.1 TWh |
| Mexico | 6.9 W | 0.2% | 0.9 TWh |
| Senegal | 6.1 W | 1.3% | 0.1 TWh |
| Russia | 5.8 W | 0.1% | 0.8 TWh |
| Laos | 5.2 W | 0.1% | 0.0 TWh |
| Lebanon | 5.2 W | 0.7% | 0.0 TWh |
| Myanmar (Burma) | 5.0 W | 1.1% | 0.3 TWh |
| Kenya | 4.8 W | 1.9% | 0.3 TWh |
| Moldova | 4.6 W | 0.3% | 0.0 TWh |
| Gabon | 4.0 W | 0.3% | 0.0 TWh |
| Burkina Faso | 3.9 W | 2.7% | 0.1 TWh |
| Mozambique | 3.9 W | 0.7% | 0.1 TWh |
| Zambia | 3.9 W | 0.4% | 0.1 TWh |
| Puerto Rico | 3.1 W | 0.1% | 0.0 TWh |
| Mali | 2.9 W | 1.5% | 0.1 TWh |
| Côte d’Ivoire | 2.9 W | 0.8% | 0.1 TWh |
| United Arab Emirates | 2.8 W | 0.0% | 0.0 TWh |
| Malawi | 2.4 W | 2.7% | 0.1 TWh |
| Sudan | 2.2 W | 0.6% | 0.1 TWh |
| Sub-Saharan Africa | 1.9 W | 0.5% | 2.4 TWh |
| Cambodia | 1.7 W | 0.1% | 0.0 TWh |
| Congo - Brazzaville | 1.6 W | 0.2% | 0.0 TWh |
| West Virginia | 1.4 W | 0.0% | 0.0 TWh |
| Cameroon | 1.4 W | 0.5% | 0.0 TWh |
| Angola | 1.4 W | 0.3% | 0.1 TWh |
| Syria | 1.3 W | 0.1% | 0.0 TWh |
| Tanzania | 1.1 W | 0.6% | 0.1 TWh |
| Morocco | 1.1 W | 0.1% | 0.0 TWh |
| Egypt | 1.0 W | 0.1% | 0.1 TWh |
| Madagascar | 1.0 W | 1.1% | 0.0 TWh |
| Papua New Guinea | 1.0 W | 0.2% | 0.0 TWh |
| Burundi | 0.7 W | 2.0% | 0.0 TWh |
| Ghana | 0.6 W | 0.1% | 0.0 TWh |
| Chad | 0.5 W | 2.6% | 0.0 TWh |
| Iran | 0.3 W | 0.0% | 0.0 TWh |
| Congo - Kinshasa | 0.3 W | 0.2% | 0.0 TWh |
| Nigeria | 0.3 W | 0.1% | 0.1 TWh |
| Ethiopia | 0.1 W | 0.1% | 0.0 TWh |